Robots of Today
“Robot” Etymology
The word "Robot" comes from the 1921 play "R.U.R." (Rossum's Universal Robots)by the Czech writer Karel Capek (pronounced"chop'ek"). "Robot" comes from the Czech word "robota", meaning "forced labor."
The word "robotics" also comes from science fiction - it first
appeared in the short story "Runaround" (1942) by Isaac Asimov.
appeared in the short story "Runaround" (1942) by Isaac Asimov.
Robots and Ethics
Isaac Asimov’s 1983 novel “I Robot”
* Law Two:
A robot must obey orders given it by human beings,
except where such orders would confict with a higher order law.
* Law Three:
A robot must protect its own existence aas long
as such protection does not conflict with
higher order law.
Robots and Ethics
* Law Zero: The robot stories of Isaac Asimov
introduced the "three laws of robotics." Later, he added
the "zeroth" law.
A robot may not injure humanity, or, through inaction,
allow humanity to come to harm.
* Law One:
A robot may not injure a human being, or,
through inaction, allow a human being to come to harm,
unless this would violate a higher order law.
* Law One:
A robot may not injure a human being, or,
through inaction, allow a human being to come to harm,
unless this would violate a higher order law.
A robot must obey orders given it by human beings,
except where such orders would confict with a higher order law.
* Law Three:
A robot must protect its own existence aas long
as such protection does not conflict with
higher order law.
Robots and Ethics
Steven Spielberg’s “Artificial Intelligence”


Dean Kamen invented what he calls “the




 Drive robot manually via web browser with
live
Drive robot manually via web browser with
live
 Built in proximity sensors can be toggled
on or off
Built in proximity sensors can be toggled
on or off
 Archive video on demand or via schedule
Archive video on demand or via schedule
 Control access to robot and video feed via
multiple
Control access to robot and video feed via
multiple
 Roving mode allows autonomous exploration
with
Roving mode allows autonomous exploration
with
 Wireless control up to 300 feet from host
Wireless control up to 300 feet from host
 Fully open source and programmable .
Fully open source and programmable .
In the beginning…
Robots were designed to be a replacement for repetitive, labor oriented tasks
Humans are slow, imprecise, prone to injury and have physical and emotional limitations.
Machines are fast, precise, durable and their limitations make them ideally suited to repetitive/dangerous tasks
Industrial Robots
The first modern industrial robots were probably
Joe Engleberger in the 1950's and 60's.
Engleberger started the first robotics company,
called "Unimation",and has been called the
Medical Robots
A human would not be able to make a
hole exactly
one 100th of a inch wide and long.
When
making medicines, robots can do the job much
faster and more accurately than.
Also, a robot can be more delicate
than a human.
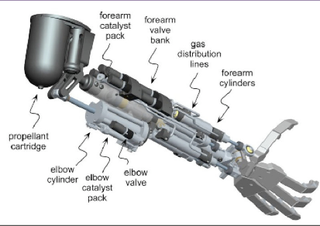
This
bionic arm can do things like picking up fragile
items such as a glass, just by
the wearer just thinking
about it.
The arm is connected directly to the brain,
so a
person can use it like any other appendage.

nElectrodes
intercept the limb's residual nerve
firings
and feed them to a computer
embedded in the
forearm, which then commands six motors
to move the device's
shoulder, elbow and hand in
unison.
Thanks to hand sensors, the wearer can even
gauge pressure and fine-tune his grip.
Dean Kamen invented what he calls “the
world’s most sophisticated robot” to transport
people with mobility impairments places they
never thought they could go.
Exploring Robots
nThe
"Odyssey IIb"
submersible robot is shown suspended in a tank.
nThe
inset shows the "Sojourner" microrover
robot being repaired. Sojourner landed on the surface of Mars on July 4,
1998 .
They
store up muscle energy, so to speak, and then they boink themselves off in various directions.
They create a cellular
communication network, on a node-to-node basis.
We're
envisioning a fleet of these little guys being sent to some promising landing
site.
Wall
Climbing and Manipulating Robot
robotic
automatic weather stations (AWS).
Security Robots
Remotec
Mine-Disposal Robots
John
Bloomfield's prototype guardian robot
nDeveloped
by SARCOS, this wearable robot suit fits
around your body like an exoskeleton,
enabling soldiers to
easily lift 200-pounds with little effort.
Security Robots
1. iRobot’s
rugged and versatile robots handle dangerous tasks and keep personnel safe .
2.Police need certain types of robots
for bomb
disposal and for bringing
video cameras and microphones
into dangerous areas, where a human policeman
might get
hurt or killed.
3.The military also uses robots for (1)
locating and
destroying mines on land and in water, (2) entering enemy
bases to
gather information, and (3) spying on enemy
troops .
Helping Robots

And one day, Tug might bring supplies to this Da Vinci surgery robot.

Robots like Boston Dynamics' Atlas can offer disaster relief where humans can't.

Harvest Automation's robots could become the new farmers

Helping Robots
The HelpMate
robots, made by the San Diego-based
Pyxis Corp., can cart around hospital
items, such as
food trays, pharmaceuticals, lab specimens, X-rays,
bandages and
blankets.
They save nurses trips to
cafeterias, pharmacies and
central supply areas.
Saves
hospitals the costs of human couriers.
Cooperative Robots
Why
build cooperating robots?
nDecreased
cost (through simpler individual robot
design)
nDecreased
task completion time (through
parallelism)
nIncreased
reliability, robustness (through
redundancy)
nIncreased
scope for missions inherently distributed in:
nSpace
nTime
nFunctionality
Characterized
as intelligent systems
that integrate perception, reasoning, and action to
perform
cooperative tasks under circumstances that
are
insufficiently known in advance, and dynamically
changing during task execution.
Cooperative robotics
nA
self-assembly and reconfiguring truss system that
can be used in construction
type activities.
Application
Domain
nmining
nconstruction
nplanetary exploration
nSimulation and modeling
nautomated manufacturing
nsearch and rescue missions
ncleanup of hazardous waste
nindustrial/household maintenance
nnuclear power plant decommissioning
nsecurity, surveillance, and
reconnaissance
Toy Robots
video feed
to assist when driving the
robot manually
user accounts
basic vision detection
computer
I, Robot




























Comments
Post a Comment